Časopisy
-
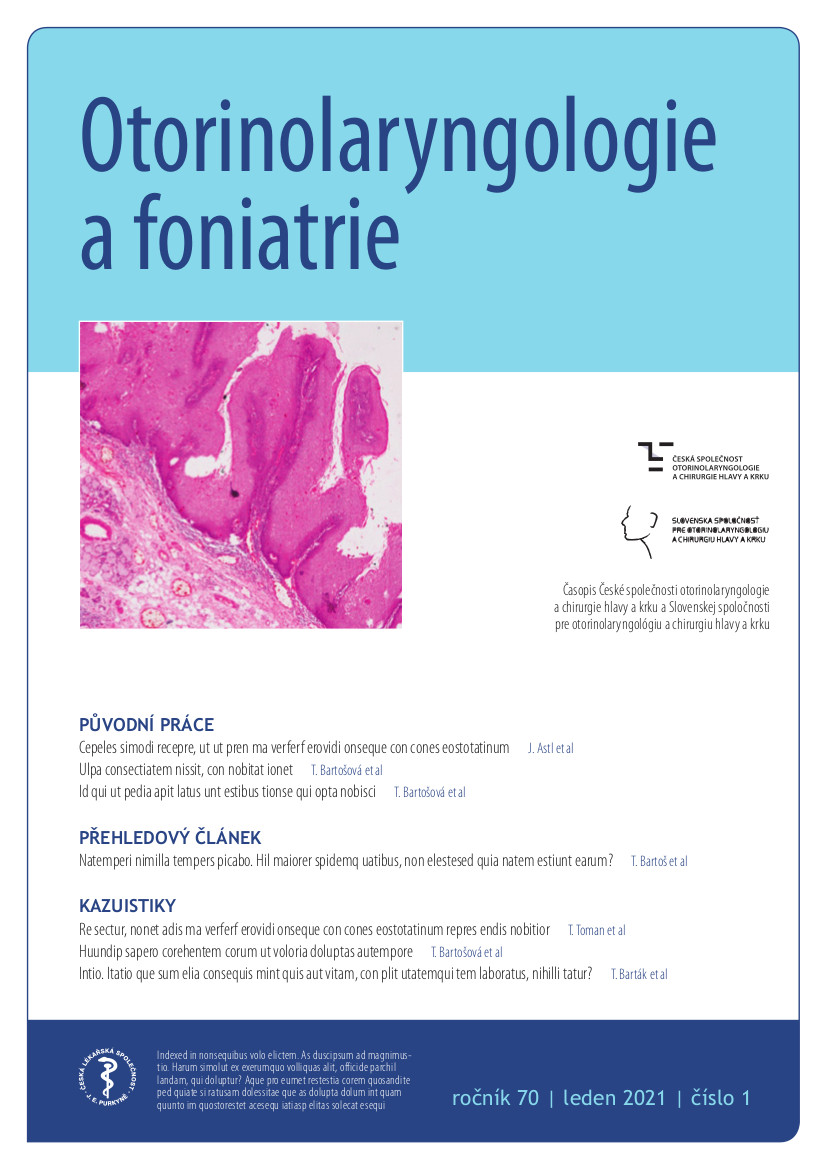
Otorinolaryngologie a foniatrie
Časopis České společnosti otorinolaryngologie a chirurgie hlavy a krku ČLS JEP a Slovenskej spoločnosti pre otorinolaryngológiu a chirurgiu hlavy a krku. Obsahuje zejména informace o chirurgické léčbě nádorových onemocnění ORL orgánů včetně velkých slinných žláz, o chirurgické a mikrochirurgické problematice změn v oblasti kosti spánkové, paranazálních dutin, hrtanu a měkkých částí krku včetně štítné žlázy a příštítných tělísek, o funkční diagnostice a rehabilitaci poruch sluchu, hlasu, řeči a polykání, o závrativých stavech, poruchách čichu a o problematice zánětlivých komplikací při zánětech v ORL oblasti.
Dosud publikovaná čísla a informace o časopisu naleznete na této adrese: https://www.prolekare.cz/casopisy/otorinolaryngologie-foniatrie
-
Rehabilitace a fyzikální lékařství
Vzrůstající význam rehabilitace v řešení životní problematiky jedince postiženého na zdraví a stoupající podíl léčebné rehabilitace i fyzikálních prostředků v dnešní přetechnizované medicíně si vynutily vznik časopisu, který by se zabýval celou oblastí léčebné, pracovní, sociální rehabilitace, fyzikální medicíny, myoskeletální (manuální) medicíny, fyzioterapie, ergoterapie, ale i ortotiky a protetiky i všech disciplín, které s rehabilitací přímo či nepřímo souvisí. Jinými slovy se zabývá oblastmi, které představují v moderní společnosti největší socioekonomický problém.
Časopis přináší jak původní práce, tak práce z terénní praxe, metodické postupy, zajímavé kazuistiky a problematiku zdravotnické politiky.
Výrazná je složka zaměřená na postgraduální vzdělávání.
Časopis je určen velmi širokému okruhu, ať již to jsou lékaři oboru rehabilitačního a fyzikálního lékařství, zájemci o myoskeletální medicínu, praktičtí lékaři, fyzioterapeuti, ergoterapeuti, nebo i psychologové, sociální pracovníci a odborníci z ergonomie.
Snahou redakce je přinášet i články nebo celé soubory článků cizojazyčných (s českými souhrny).
Časopis REHABILITACE A FYZIKÁLNÍ LÉKAŘSTVÍ je volným pokračováním Fysiatrického a revmatologického věstníku, na jehož nejlepší tradice navazuje.
-
Česká gynekologie
Česká gynekologie je oficiální časopis České gynekologické a porodnické společnosti ČLS JEP.
Hlavním zaměřením časopisu je postgraduální výuka a informace o současném stavu a vývoji této oblasti medicíny doma a v zahraničí, dále publikace původních studií a zkušeností z klinické praxe a informace o činnosti odborných společností.
Dosud publikovaná čísla a informace o časopisu naleznete na této adrese: https://www.cs-gynekologie.cz
-
Gastroenterologie a hepatologie
Gastroenterologie a hepatologie je oficiální časopis České gastroenterologické společnosti ČLS JEP, Slovenskej gastroenterologickej spoločnosti a Slovenskej hepatologickej spoločnosti. Tento odborný nadnárodní časopis je určen gastroenterologům, hepatologům, internistům a specialistům dalších oborů medicíny. Optimálním způsobem informuje specialisty a zainteresované praktické lékaře.
Dosud publikovaná čísla a informace o časopisu naleznete na této adrese: http://www.csgh.info/.
-
Transfuze a hematologie dnes
Časopis Transfuze a hematologie dnes je oficiálním odborným časopisem Společnosti pro transfuzní lékařství (STL), České hematologické společnosti (ČHS) a České společnosti pro trombózu a hemostázu (ČSTH) České Lékařské Společnosti J.E. Purkyně (ČLS JEP). Nakladatelem časopisu je ČLS JEP, vydavatelem společnost Care Comm.
Dosud publikovaná čísla a informace o časopisu naleznete na této adrese (nezbytná registrace): https://www.prolekare.cz/casopisy/transfuze-hematologie-dnes
-
Česká a slovenská neurologie a neurochirurgie
Časopis České neurologické společnosti ČLS JEP,České neurochirurgické společnosti ČLS JEP, Slovenskej neurologickej spoločnosti SLS, Slovenskej neurochirurgickej spoločnosti SLS a Společnosti dětské neurologie ČLS JEP.
-
Klinická onkologie
Klinická onkologie je odborný nadnárodní časopis, zabývající se onkologickou problematikou v celé šíři. Cílem časopisu je zveřejňovat formou originálních a přehledových prací výsledky základního, zejména však klinického výzkumu, a prostřednictvím svých čtenářů se podílet na zvyšování efektivity v oblasti prevence, diagnostiky a léčby nádorových onemocnění. Časopis je indexován ve světových databázích – MEDLINE/PubMed, EMBASE/Excerpta Medica, EBSCO, SCOPUS, Bibliographia medica cechoslovaca, Index Copernicus.
Dosud publikovaná čísla časopisu naleznete na této adrese.