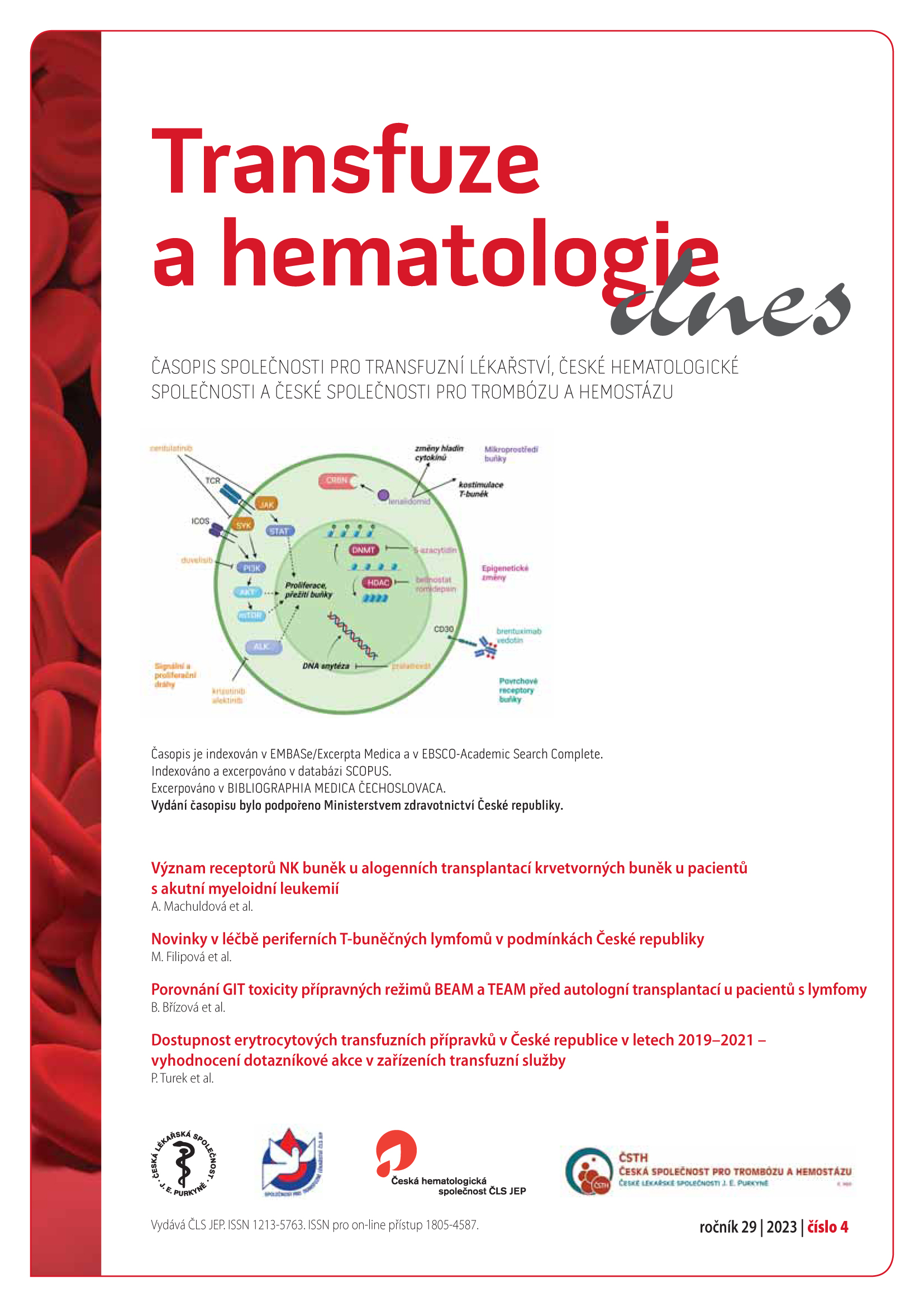
Význam receptorů NK buněk u alogenních transplantací krvetvorných buněk u pacientů s akutní myeloidní leukémií
Keywords:
akutní myeloidní leukémie, KIR, NKG2D, MICA, MICBAbstract
NK cells play important role in allogeneic stem cells’ transplantation. Not only as effector cells in the eradication of remaining cancer cells but they also affect development of the graft versus host disease. Hence, it is important to understand their regulation and how can immune system of patient affect the donor’s NK cells. NK cells’ inhibition or activation is directed by many receptors which interact with broad spectrum of ligands. Inhibition ligands signal that the target cell is healthy, activating ligands show that the cell is damaged. The mostly investigated receptors are KIR together with NKG2D receptor with its ligands MICA and MICB. This work describes their role in stem cell transplantation.